Human beings have become fully dependent on the automobile industry to enable the smooth conduct of our affairs. The world would come to standstill without the cars, buses and trucks. The factories that manufacture such vehicles have evolved tremendously since the advent of commercial manufacturing of cars in the 29th century. We’re finding increased use of advanced technologies in the automotive industry and the focus appears to be on electric cars and driverless cars. There is another technology called Augmented Reality (AR) along with Virtual Reality (VR) that has created a significant impact across the entire value chain of the automotive industry. Experts have observed that AR & VR in the automotive industry would grow by $5.1 billion in the next five years (2021-2025) at a CAGR of about 32%. Augmented Reality applications are now found in the areas such as design, production, assembly, maintenance, driver assistance, safety and marketing sectors of the automotive industry. These applications have created exciting possibilities for the industry and its consumers.
This post is going to present the wide spectrum of how we use augmented reality in the automotive industry. Please buckle up, put on some shades and enjoy this exciting ride on AR in the automotive industry.
Design & Prototype Development
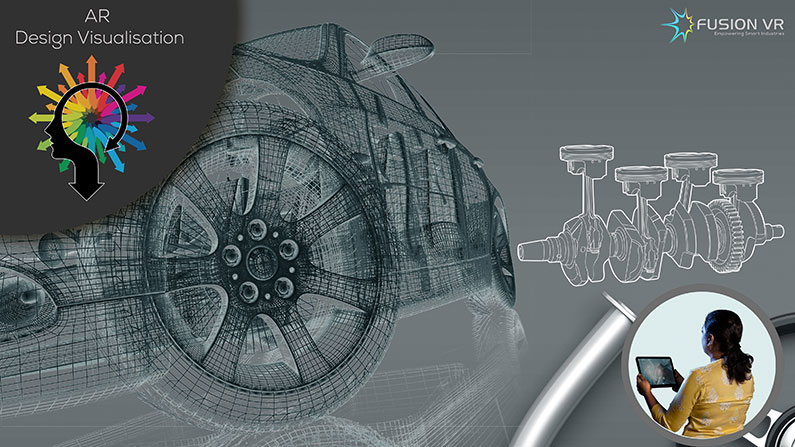
Let’s begin with Augmented Reality applications in automotive industry during the design and prototype development of any automobile. Car manufacturers tend to reduce the overall development duration so that models are brought to market sooner than their competitors. As you are aware, designing and building a new prototype is often a costly and time-consuming process in automotive manufacturing. It is also important to highlight the importance of a good, high quality design is a key factor in the success of any car model. The visual appeal of the design highly influences the purchasing decision of a prospective car buyer. Engineers and designers use AR-powered Tablet & wearable Solutions to develop rudimentary AR prototypes to showcase design variants with virtual components, eliminate physical mock-ups and enabling the design team to have real-time collaborative design reviews on a virtual 3D model. The virtualization of the prototype enables team members from remote locations to participate and contribute towards the review and finalization of a design. The model developed can be rendered as a life-sized Photorealistic Virtual 3D model within a reasonable short duration thereby eliminating resource and cost constraints associated with physical modeling. Major automobile manufacturers across the world are utilizing augmented reality applications to strengthen, streamline and upgrade their design approaches and create a positive impact with their products in the marketplace.
Manufacturing
Moving from design, let us explore the use of AR in the production and assembly of automobiles. AR wearables are being used to digitally overlay essential and critical information to assemble to various components. With increased digitalization in the automobile, the integration of various systems with the electronics and user interface requires careful and proper assembly. A major problem during automotive assembly is aligning the exterior car panels within the specified design tolerances. Such tasks can be supported with AR applications that guide manufacturing teams to do it right. Rework due to incorrect integration and assembly often consumes significant resources at considerable cost which can be effectively avoided using AR driven digital tools. Step by step instructions, guidance and remote assistance with the use of head mounted displays can be provided. This helps to immediately address problems at an incipient stage before they become issues leading to assembly line downtime and impact the entire supply chain. In addition to that, other manufacturing and business applications such SAP can be integrated to make better shop-floor decisions. Manufacturing managers, engineers and quality controllers must learn to leverage AR & VR in the automotive industry to achieve manufacturing excellence.
Learning & Development
People are often referred to as human capital these days and as we all know well, they are vital to the success of any enterprise and the automotive industry is no exception. Highly trained and competent workers is the dream of many industry captains and it is obvious that large factories are located near cities with a readily available pool of technical labor from universities and polytechnics. Despite these advantages, employees need to be trained before being deployed to assembly lines or shop floors.
Traditional training methodologies such as classroom instruction followed by field visits often does not deliver on the established learning objectives of many companies. The impact of poor training and learning becomes evident when employees are assigned to the units. Lower productivity, increased rework, wastage and customer complaints are all related to employee training and competence assessments. Augmented Reality technologies have now created solutions such as Maintenance Training Simulators (AR-MTS) using AR powered Tablets that augment the immersive Digital Twin of the sophisticated automobile systems right inside a classroom training environment. Training includes picking the right parts and tools aided by step-by-step instructions from Standard Maintenance Procedures (SMP) along with clear internal views of the equipment handled. This augmented hands-on experience enables better understanding and retention of concepts, procedures and techniques to efficiently operate and maintain sophisticated machinery and tools in the factory. Workers also experience pride with the skills developed and become useful contributors at work. This is another key area of applying augmented reality in automotive training.
Maintenance Support

The augmented reality applications developed for training can also be deployed to provide the assistance needed while performing maintenance tasks. Tablets and other wearables provide not only the necessary information, but also real time data on spares, consumables and other resources needed to complete the task. This helps to reduce the incidence of errors during execution enabling timely completion, reduced downtime and achievement of production targets.
Safety Excellence
Safety Performance is of the highest priority across many companies. The safety of employees and assets can be enhanced with the use of AR and VR in the automotive industry. Training personnel on using safe work practices and in the planning and response to emergency situations is critical. Augmented Reality applications using wearables can maximize the effectiveness by speeding up the team’s response time through smart-instructions using voice, text and infographics.
Marketing & Customer Support
Further down the automotive industry value chain after design and manufacturing is marketing and customer experience with vehicles. Augmented reality can enhance the marketing and customer experience with virtual Showroom solutions that help car dealerships positively influence customers. AR applications enable the virtual configuration of the exterior and interior of the cars as desired by customers helping them make buying decisions by visualizing and virtually experiencing the desired features, add-ons and variations. A customer can decide on the color of the exterior, the type of interior furnishings, colors, external mountings, bumpers etc. before swiping that card. All of these and more can be again achieved with the use of handheld tablets and wearables.
Enhanced Driver Experience

Another aspect of the customer experience of augmented reality in vehicles is when using it and enhancing the driver experience. Drivers can be provided additional information embedded on the windshield on traffic conditions, weather reports, driving speed, local environment etc. This does not divert the driver’s attention away from the road and helps the driver take precautionary measures and change driving behaviors to minimize the occurrence of incidents and injuries to the most vulnerable road users. All of this helps with safe and pleasurable driving experience for the customer and the family. In the event of a breakdown on a highway or remote area, AR enabled support applications on a smart phone or tablet provide detailed instructions from an experienced technician and help the customer troubleshoot the problem. Also identifying the correct issue helps deploy the right technicians and tools to the breakdown site and render assistance effectively.
Conclusion
As we draw a close to this journey on the applications of augmented reality, one can appreciate the extent to which AR is being applied in the automotive industry. The question as to what are the applications of augmented reality has been reasonably addressed. More and more use cases are being identified that reinforce the value and potential of augmented reality for the automotive industry. Whether you are an industry consultant, manufacturing expert or a customer, it is clear now about how this technology creates in making automotive industries smarter, safer, productive and also benefiting customers throughout the lifecycle of the vehicle.




